Pigmentation
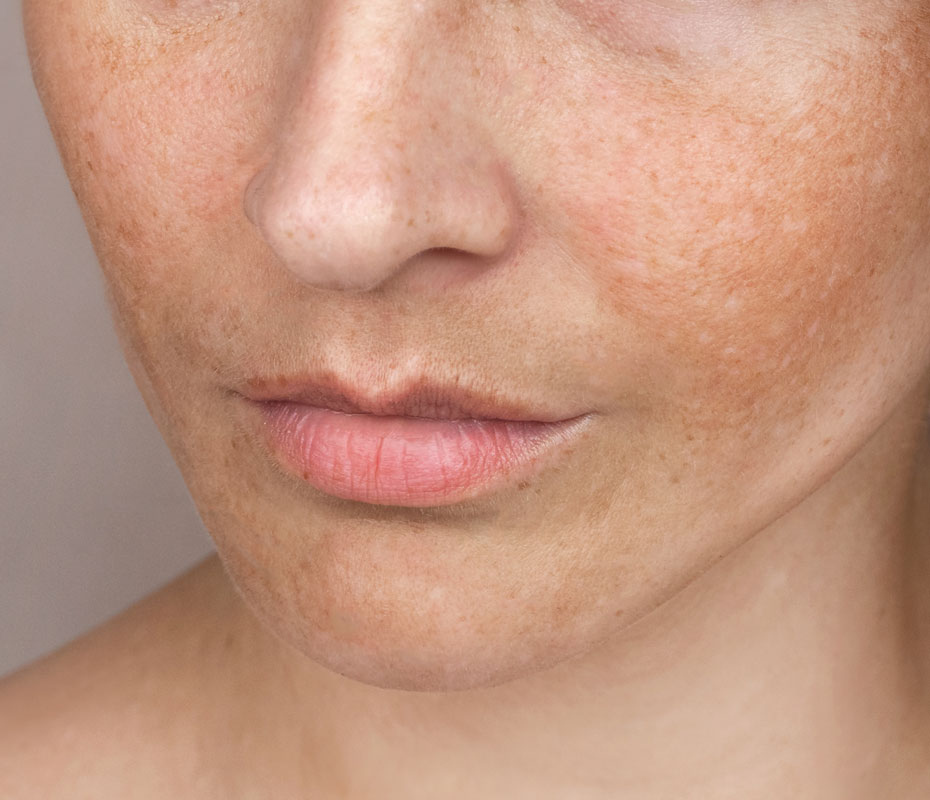
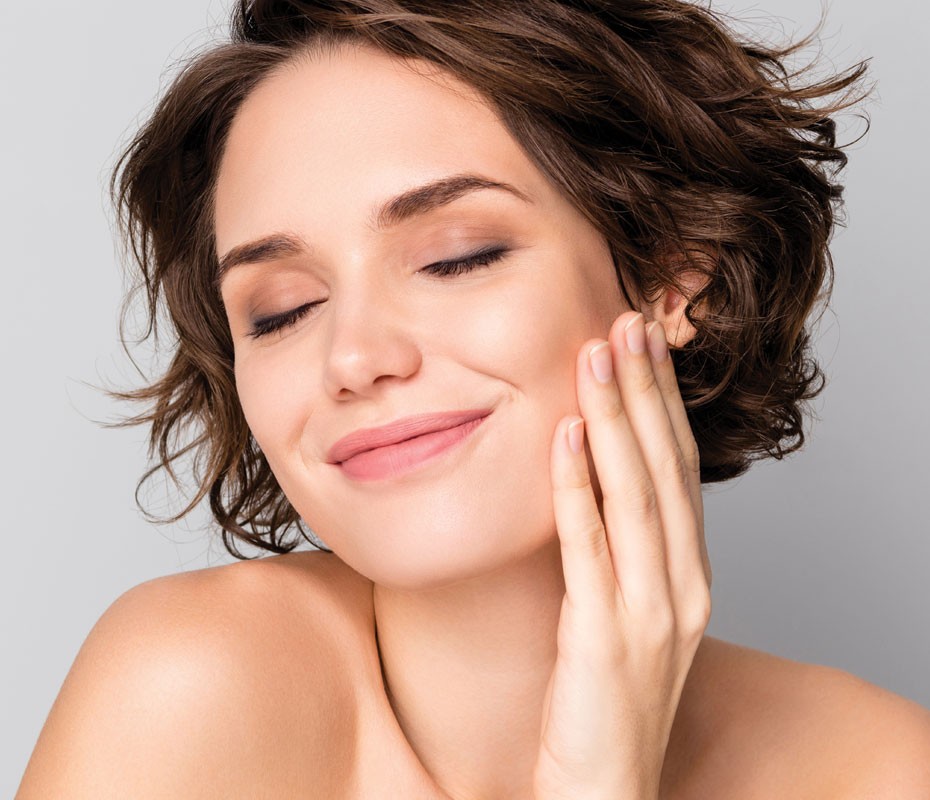
Pigmentation refers to the colouring of the skin. Skin pigmentation disorders occur when there is an abnormality in the melanin (the pigment that gives skin its colour) production in the body, leading to patches of skin that are either darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation) than the normal surrounding skin. Imbalances and disorders of the skin can lead to inconsistent colouration, patterning, and ‘blotches’. Uneven skin tone is a common manifestation of pigmentation disorders, impacting the ability to achieve an even-toned complexion.

What Causes Pigmentation? Sun Exposure and Other Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of pigmentation disorders, including:
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays can increase melanin production, leading to sunspots or age spots.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like melasma can occur due to hormonal changes during pregnancy or from taking oral contraceptives. Certain hormonal changes can cause the skin to darken without sun exposure.
- Inflammation: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) can result from skin injuries or conditions such as acne.
- Genetics: A family history of pigmentation disorders can increase the likelihood of developing these conditions.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause pigmentation changes as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions: Diseases such as Addison’s disease or vitiligo can cause pigmentation changes.
- Ageing: Natural ageing processes can result in pigmentation changes, often appearing as age spots.
Understanding the specific cause or combination of causes is crucial in effectively treating pigmentation disorders. Consulting with a specialist can provide a tailored treatment plan based on your specific condition and lifestyle. Hyperpigmentation can fade over time with treatment but some cases may persist without intervention.
Characteristics of Pigmentation: Understanding Melanin Production
- Hyperpigmentation: Darker patches of skin, often brown, black, or grey. Topical treatments can be effective in reducing these darker patches of skin.
- Hypopigmentation: Lighter patches of skin, appearing white or lighter than the normal skin tone.
- Distribution: Can occur in isolated patches or spread over larger areas.
- Skin Types: People with darker skin types tend to have more melanin in their skin cells than those with lighter skin.
How Can You Treat Pigmentation? Methods to Treat Skin Pigmentation
Various treatments can help reduce the appearance of pigmentation disorders. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity and underlying cause. Here are some common approaches:
Lifestyle Changes:
- Sun Protection: Regular use of sunscreen can prevent further pigmentation changes.
- Proper Skincare Routine: Using gentle skincare products to avoid further irritation and inflammation.
Skincare Products:
- Topical Treatments and Lightening Agents: Products containing ingredients such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, and vitamin C can help lighten hyperpigmented areas.
- Exfoliants: Products containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) can help remove dead skin cells and improve skin tone.
- Retinol: Retinol can be effective in reducing hyperpigmentation by accelerating cell turnover.
- Natural Remedies: Ingredients like aloe vera, green tea extract, and liquorice extract can improve hyperpigmentation without completely eliminating it.
Medical Treatments:
- Chemical Peels: These can remove the top layer of skin, helping to reduce pigmentation.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target and break down pigmentation.
- HydraFacials: This non-invasive treatment exfoliates the skin, helping to reduce pigmentation.
- Microneedling: This treatment can stimulate collagen production and help with pigmentation.
- Broad Band Light (BBL) Therapy: Uses light energy to target and reduce pigmentation.
Complimentary treatments
What to expect
- 30-minute consultation with an aesthetician
- Proprietary triage system guaranteeing referral to the most suitable practitioner
- Treatment carried out at Montrose London, a leading specialist skin aesthetics and plastic surgery clinic
- Dedicated Patient Co-ordinator as a personal point of contact throughout your journey at Montrose London
- Comprehensive post-treatment aftercare by our expert doctors and aestheticians
Thank you
Overall a disappointing experience, sterile and cold enough environment made bearable only by the maximalist decor. No serenity as portrayed in marketing features ie. Lack of music As a director within a private healthcare setting, very poor customer experience and not one I will be recommending to our own clientele.
I was advised if unhappy with results in 2 weeks to come back for a top up but work restrictions meant I did not attend for 4 weeks but was told that this was chargeable: disappointing again with lack of appreciation or flexibility for working professionals. No follow up provided or courtesy call as is often given at alternative aesthetic clinics.
Dr. Noy has been incredible from start to finish. It is a joy to go to this beautiful clinic, and care is second to none.